RAS Know-how Knowledge in a nutshell

Was ist eigentlich Schwenkbiegen?
Bei welchen Biegeteilen eignet sich Schw...
Schnelles Rüsten
Einfaches Handling
UpDown-Schwenkbiegen mit Pendeln und Umf...
UpDown-Schwenkbiegen mit einer oder zwei...
Radien biegen
Schwenkbiegen von Edelstahl und beschich...
Schwenkbiegen von Lochblech, Streckgitte...

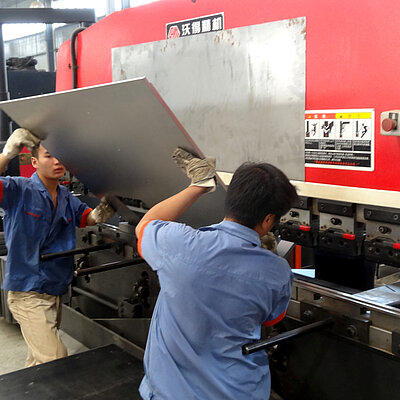
Bending sequence
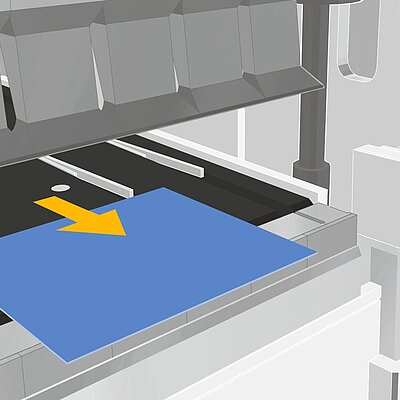
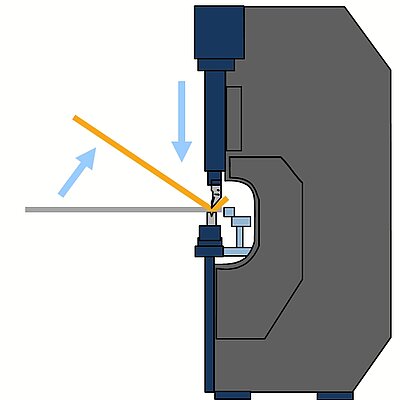
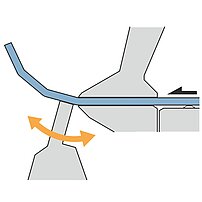
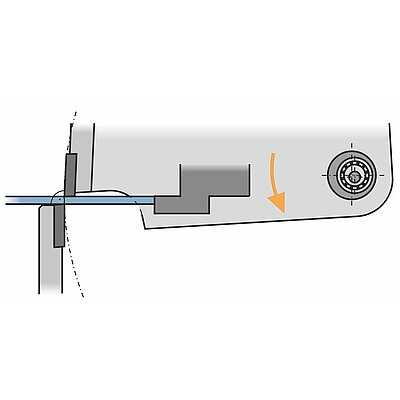
Folding
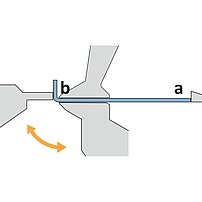
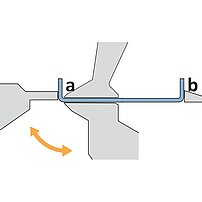
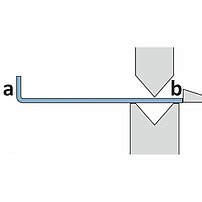
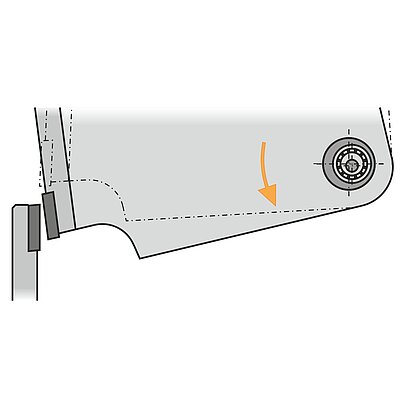
During the folding sequence the blank rests on the sheet support table. A gauging system positions the part to the bend line. The upper and lower beam clamp the blank. During the bending cycle the folding beam moves up around a pivot point. On up-down acting machines, the folding beam moves upwards or downwards, depending on the bending direction.
- The part rests on the table (no fatigue, short cycle times)
- The gauging system positions the part to the bend line (operator training finished in no-time)
- Upright posture, easy operation (no health problems)
- Usually one operator is sufficient even for large, cumbersome and heavy parts (low labor/parts costs)
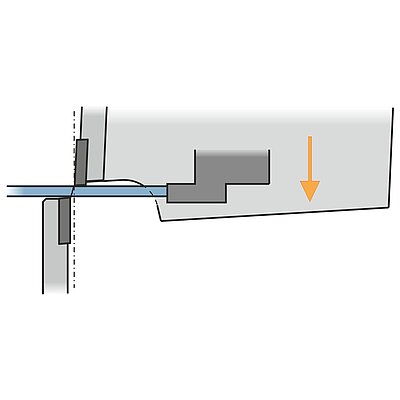
Bending sequence
Press brake
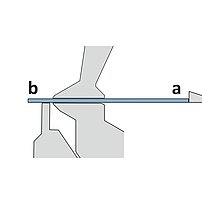
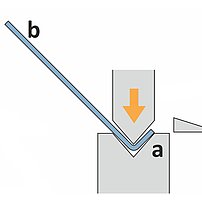
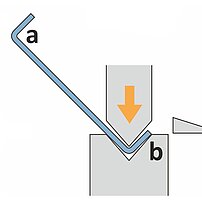
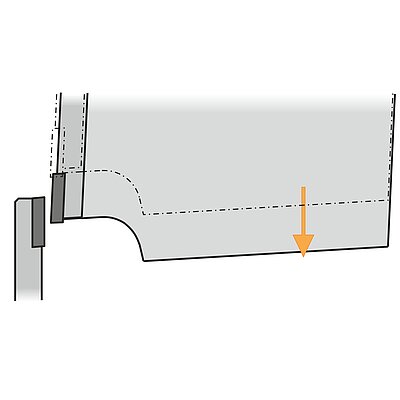
During the bending sequence the blank is positioned outside the machine. The operator holds and supports the weight of the blank. For bending the upper ram moves down into the lower die. Both sides of the part move up and leave the plane. A linear ram movement results in the bend angle. Sequence requires experienced operators.
- Operator needs to lift/support/hold the part (quality problems due to fatigue)
- Experienced, well trained operator required (problem finding skilled operators)
- Health (shoulder problems) and safety are critical
- Large/cumbersome or heavy parts require multiple operators (high costs per part)
- Slow cycle times (high costs per part)
Machine setup
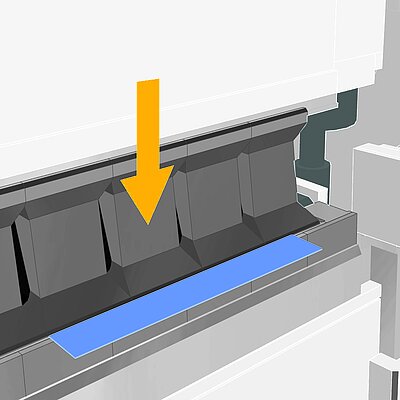
Folding
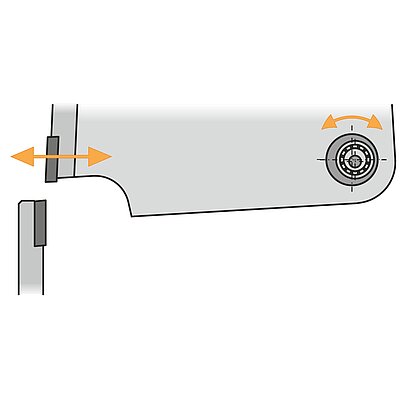
Folding machines can bend all angles with a single set of tools. The machine automatically adjusts to the material thickness. Higher automated folding machines come with an automatic tool changer.
- Universal tools (reduced setup effort)
- Usually one set of tools sufficient for all customer parts
- Low investment and operating costs
- Low set-up times allow for small batch sizes (need-based production)
Machine setup
Press brake
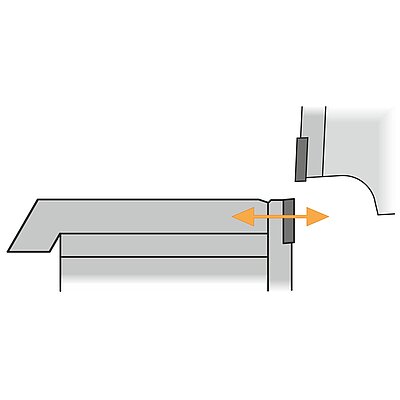
Press brake bending typically requires a large number of punches and different applications.
- Different "V" dies for different sheet thicknesses
- Small "V" dies required for short flanges
- Usually a large variety of upper ram geometries are used
- Investment in additional tools over time
- Often long set-up times
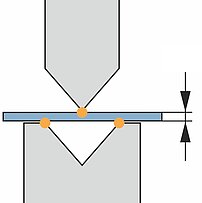
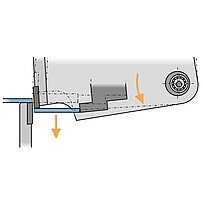
Material thickness tolerances
Folding
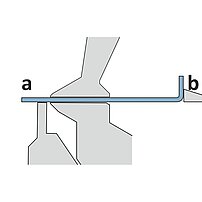
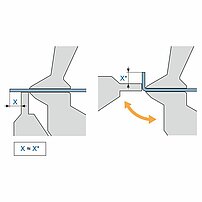
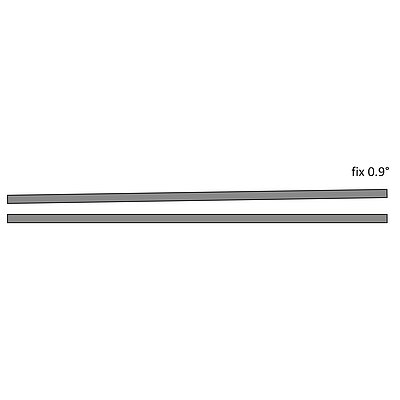
During the folding sequence the folding beam tool contacts the outside of the material and moves exactly to the programmed angle.
- The reference side is only the outside of the material
- Exact movement to the programmed angle (high angle accuracy)
- Sheet thickness tolerances do not affect the bend angle
- No angle measuring system required
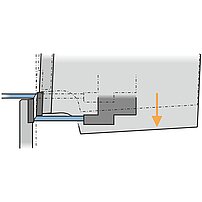
Material thickness tolerances
Press brake
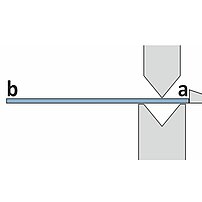
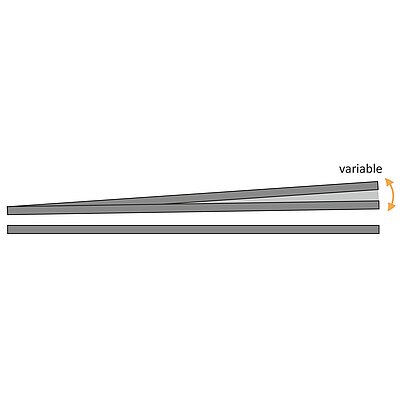
On press brakes, the punch contacts the material from above and the "V" die from below.
- Contact points on both sides of the material
- The bend angle iresults from a linear upper tool movement
- Sheet thickness tolerances lead to angle variances
- Expensive, inflexible angle measuring system required for compensation
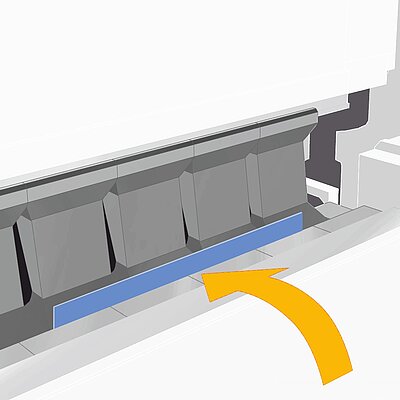
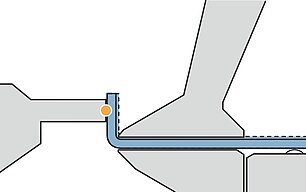
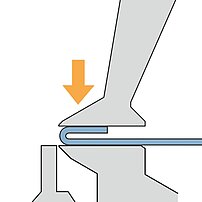
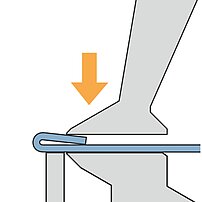
Gauging
Folding
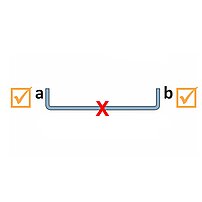
On a folding machine the entire part is inside the machine. Only a short flange stands out of the upper and lower beam tool.
- Gauging of the entire part
- Blanks dimension tolerances show up in the first flange
- The overall panel dimension as well as the opposite flanges are always accurate
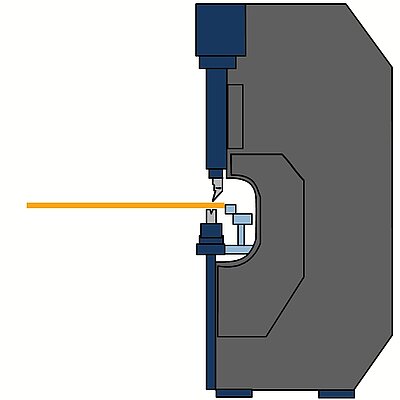
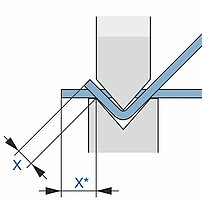
Bending radii
Folding
On folding machines, a radius can be easily created of short bending segments. By using small steps the outside of the radius will be very smooth and the individual steps will not be visible.
- Creation of any radius without special tools
- Bending steps not visible on the outside
- Part rests on the table
- Fast bending cycles